Relativity stands as one of the most transformative theories in the history of physics. Developed by the genius physicist Albert Einstein, the theory of Relativity reshaped our understanding of space, time, and gravity. In this article, we explore the depths of Relativity, its foundational concepts, and its significance in modern physics. This comprehensive discussion is brought to you by Physics Heaven, your source for in-depth physics explorations.
The Foundations of Relativity
Relativity is composed of two primary theories: Special Relativity and General Relativity. Each of these theories revolutionized physics by introducing groundbreaking concepts that challenged classical mechanics.
Special Relativity
Special Relativity, introduced in 1905, focuses on the physics of objects moving at constant speeds, particularly those approaching the speed of light. It introduced two pivotal ideas:
- The Principle of Relativity: The laws of physics are the same for all non-accelerating observers.
- The Constancy of the Speed of Light: The speed of light in a vacuum is constant and independent of the motion of the light source or observer.
Special Relativity led to astonishing conclusions, such as time dilation (moving clocks run slower) and length contraction (moving objects appear shorter along the direction of motion).
General Relativity
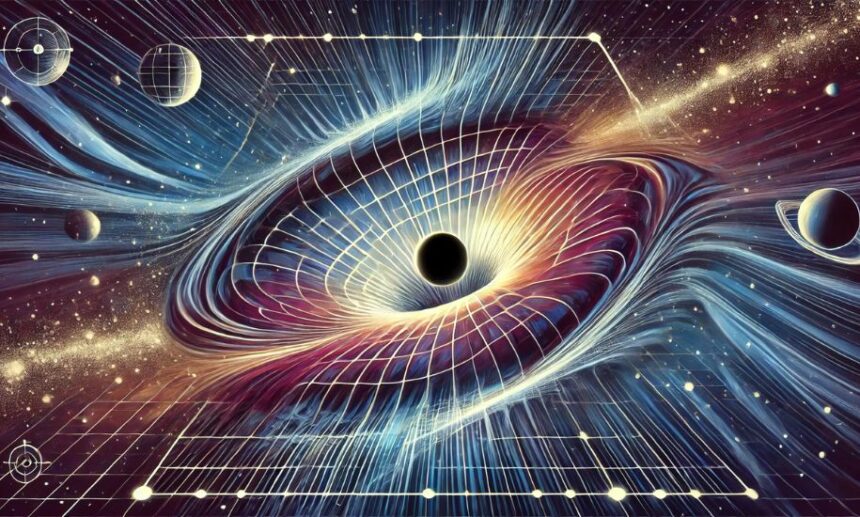
General Relativity, published in 1915, extended the principles of Special Relativity to include gravity. Einstein proposed that massive objects distort the fabric of space-time, and this curvature guides the motion of other objects. This concept replaced the Newtonian idea of gravity as a force with the understanding that gravity is the effect of curved space-time.
Key Concepts in Relativity
Space-Time Continuum
Relativity introduced the idea that space and time are interconnected, forming a four-dimensional continuum. Events in the universe occur within this fabric, and the presence of mass and energy can warp it, affecting the motion of objects and the flow of time.
Time Dilation and Length Contraction
Special Relativity predicts that time slows down for objects moving close to the speed of light, known as time dilation. Likewise, these objects also experience length contraction, appearing shorter along the axis of motion from a stationary observer’s perspective.
Mass-Energy Equivalence
Perhaps the most famous equation in physics, E=mc², stems from Relativity. This equation shows that mass and energy are interchangeable, highlighting the immense energy stored within matter.
Practical Applications of Relativity
Though Relativity might seem abstract, its principles have real-world applications. One everyday example is the Global Positioning System (GPS). GPS satellites account for both Special and General Relativity to provide accurate location data, as time moves differently for satellites in orbit compared to observers on Earth.
Another application is in nuclear energy, where mass-energy equivalence explains how a small amount of mass can release vast amounts of energy in nuclear reactions.
Relativity and the Cosmos
Relativity is fundamental to our understanding of the universe. General Relativity predicts phenomena such as black holes, regions of space where gravity is so intense that nothing can escape. It also explains gravitational waves, ripples in space-time caused by violent cosmic events, which have been directly detected by observatories like LIGO.
Additionally, Relativity provides the foundation for cosmology, helping scientists understand the Big Bang, cosmic expansion, and the behavior of galaxies.
Challenges and Advancements Beyond Relativity
While Relativity has passed every experimental test to date, it does not fully explain the universe. Notably, it does not reconcile with quantum mechanics, the theory governing the behavior of particles at the smallest scales. Physicists are working towards a unified theory, sometimes called quantum gravity, that would merge these two frameworks.
Efforts such as string theory and loop quantum gravity aim to bridge this gap, though a complete theory remains elusive.
Why Relativity Matters Today
Understanding Relativity is crucial for both theoretical and applied physics. It challenges our perception of reality, showing that time and space are more dynamic and interconnected than once thought. At Physics Heaven, we believe that grasping these profound concepts can inspire the next generation of scientists and innovators.
Relativity also encourages technological advancement, informing areas from space exploration to quantum computing. Its principles remain at the frontier of scientific discovery, pushing the boundaries of what we know about our universe.
Conclusion
Relativity is more than a scientific theory—it is a gateway to understanding the fundamental nature of the universe. From the bending of space-time to the unification of mass and energy, its concepts continue to transform science and technology. Physics Heaven is proud to delve into these fascinating topics, illuminating the wonders of Relativity for all curious minds.